In an era where reliable connectivity enables us to do just about everything, it’s easy to get confused by the proliferation of wireless technologies available today. Two you may’ve heard rumblings about lately are Cel-Fi and Wi-Fi 7 but despite their similar names, they’re intended to accomplish very different things.
This manual explains what each technology does, the pros and cons of each and how to choose which best fits your business or property.
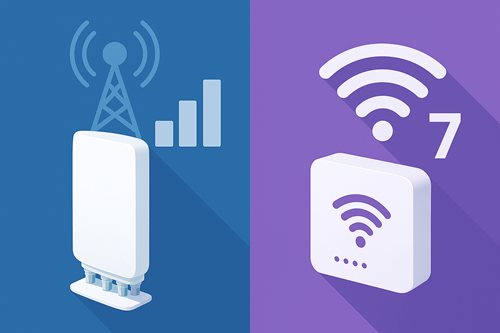
What is Cel-Fi?
Cel-Fi is a cell signal booster designed to improve mobile signal inside. It picks up a weak mobile signal from the nearest network mast, amplifies it and redistributes it around your building. Cel-Fi systems are particularly useful where mobile reception is spotty, rural locations, large buildings with solid walls, or underground structures.
Advantages of Cel-Fi
Boosts mobile signal: Strengthens weak cellular signals from operators like EE, O2, Three and Vodafone.
- Better call quality: Reduces call drops and voice interruptions.
- Faster mobile data: Supports 3G, 4G and 5G speeds where the original signal was weak.
- Longer battery life: Less power is used in maintaining a good signal.
- Carrier-approved: Cel-Fi is legal and approved by carriers in UK network law.
Disadvantages of Cel-Fi
- Needs existing signal: It can’t create coverage where there is no outdoor signal.
- Boosts limited space: The increased coverage only covers as far as the internal antenna can transmit.
- One-carrier units: Some units are intended for a single mobile carrier.
What is Wi-Fi 7?
Wi-Fi 7 is the latest generation of wireless internet technology. It is also referred to as IEEE 802.11be. It’s designed to provide extremely high speed and lower latency on a local network. It is quite ideal for applications that require high bandwidth, including video calling, streaming, online gaming and smart building applications.
Benefits of Wi-Fi 7
- Extremely high speeds: Up to 4.8× faster than Wi-Fi 6.
- Lower latency: Ideal for applications with real-time requirements such as AR, VR and live streaming.
- Better capacity: Can support multiple devices nearby simultaneously.
- Better stability: New tech reduces interference and lost connections.
Downsides of Wi-Fi 7
- Requires compatible devices: You’ll need newer hardware and routers to get the most out of it.
- Only for local networks: Wi-Fi 7 connects devices to your internet router, not mobile networks.
- Shorter range at high speed: Speed decreases with distance and obstacles.
Cel-Fi vs Wi-Fi 7: What Should You Use?
It simply matters what kind of connectivity problem you’re solving:
Choose Cel-Fi if you’re experiencing weak or patchy mobile reception within. It’s the ideal solution for delivering seamless voice calls, texts and mobile data coverage across your building.
Choose Wi-Fi 7 if you require higher internet speeds, reduced latency and better performance for your home, warehouse, or office network.
In others, they complement each other — Cel-Fi keeps your mobile devices in touch with the network and Wi-Fi 7 delivers high-speed localised access to the internet.
Need Help Choosing the Right Solution?
We create and deploy solid connectivity solutions to diverse industries including healthcare and education, utilities, defence and transport.
Whatever you need, whether it is better mobile coverage with Cel-Fi or at the cutting edge of Wi-Fi performance with Wi-Fi 7, our experts can consult and install the solution you need for your site.
Contact us today to discuss your requirements and receive the optimum connection solution for your company.